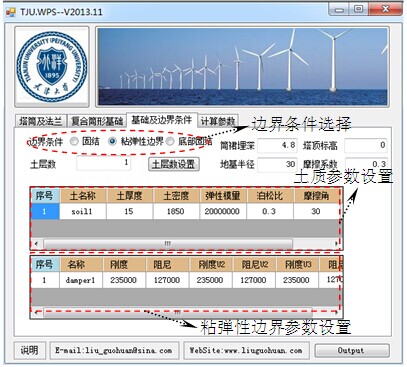
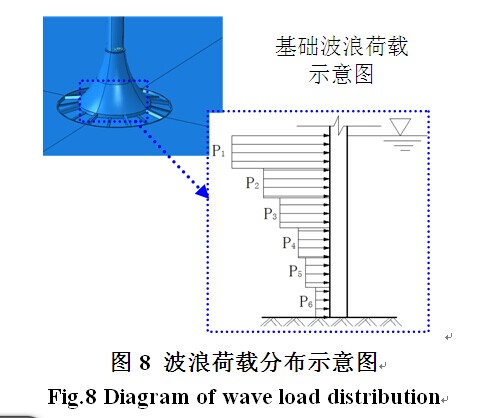
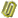地震与波浪共同作用下近海风电结构相应及倒塌模式作者: 柳国环,练继建,于通顺 |
||||||
下载次数:
次 更多论文下载...
2016年24卷第1期
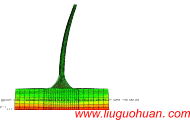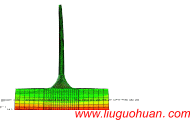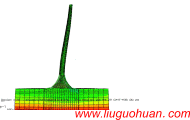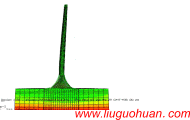
摘要:近海风力发电结构在极端地震作用下反应数值模拟涉及几方面问题:塔筒-基础-地基-边界系统有限元模型建立的合理与便利性;地震作用下联合波浪力作用;不同地震波对风电结构体系的不同作用特点。首先,开发了塔筒-筒型基础-地基-透射边界的可视化智能建模程序TJU.WPS (Wind Power Structure)。然后,计算分析大震和波浪联合作用的风力发电结构动力响应,研究结构体系的地震反应对波浪力和不同地震波的敏感性;最后,分析超大震作用下风力发电结构的倒塌破坏模式。结果表明:(1)开发的TJU.WPS程序界面友好方便、快捷、实用可靠;(2)分析并解释了天津波、迁安波和Taft波三种典型地震动及联合波浪力共同作用时风机结构振动的频谱特性,强调了波浪力的不容忽视性:与单独输入地震波相比,波浪力能够显著改变结构动力响应功率谱中能量的分布;(3)论述了三种典型地震动作用下风机结构体系的破坏模式相同点及其区别:超大震作用下风机结构都将脱开地基向上运动,最终回落到地基,但是不同典型地震动下风机结构脱开地基对应的时刻不同。计算结果给出了引起风机结构倒塌破坏不同典型地震动的最小峰值。
关键词:近海风力发电结构;地震;复合筒型基础;波浪力;倒塌 中图分类号:P315.9;U442 文献标识码:A 文章编号: Abstract: Seismic simulation for the offshore wind structure system involves in the several aspects: the reasonability and convenience for establishing FEM model of the offshore wind structural system of tower tubes-foundation-soil-transmitting boundary; the response of wind structure under earthquake combined with waves force; the response of wind structure under different type of earthquake waves. In this paper, a visual intelligent program called TJU.WPS (Wind Power Structure) for establishing tower tubes-foundation-soil-transmitting boundary is coded and developed successfully. Then, the dynamic characters of structural system is analyzed and explained in theory considering the excitation characteristics, and the sensitivity of the response to wave force and different earthquake waves is analyzed comprehensively. At last, the structural modes of failure are analyzed by selecting unfavorable earthquake wave. Analysis results show that :(1) The developed program TJU.WPS is not only easy to operate , practicable and reliable; (2)The characteristic of the response of wind structure under Tianjin wave, Qianan wave and Taft wave combined with wave force based on frequency field is explained respectively. It is emphasized that wave force can significantly change the energy distribution in the power spectral density (PSD) of the structure of the dynamic response, and it cannot be neglected; (3) The sameness and difference of modes of failure under three typical earthquake waves is discussed that the wind structure disengages soil, then falls to the ground under huge earthquake, and the time that wind structure disengages soil under different earthquake waves is different. The minimum magnitude of Tianjin wave, Qianan wave and Taft wave that causes failure is pointed out. Keywords: Offshore wind power structure; earthquake; composite bucket foundation; wave force; failure 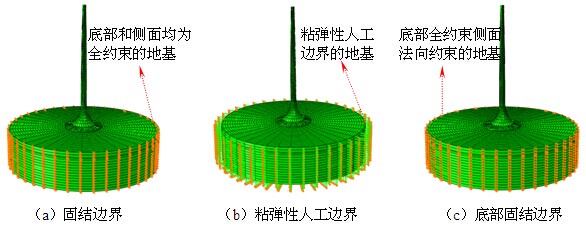 引言 近海风力发电结构是一种清洁能源结构体系,目前已在沿海地区建设且规模日趋庞大。海上风电结构体系处于复杂的环境中,承受的外界自然激励复杂多样。国内外专家关于这种结构体系在风、浪、流、地震单一荷载作用下及风、浪、流多荷载作用下的动力响应研究已经做了不少研究[1-5]。但是对于风力发电结构体系,在地震作用下,会引起基础上的动水压力变化[6],尤其是地震作用下考虑次生灾害波浪力多激励作用下动力反应、破坏以及倒塌模式的研究少见于公开发表文献,甚至关于开展这项研究的意义和内容尚未引起足够的重视和关注。 从整体角度分析,海上风电结构是一种典型刚柔复合型结构体系:塔筒质量分布较为均匀,具有高、柔特性,而基础质量集中、体积大、刚度强。这样物理形式的结构体系,在数学意义层面则直接决定其固有的动力特性:(1)低阶振型主要为塔筒振动,体现低频长周期特性,对低频段激励敏感而容易引发共振;(2)相对的高阶振型体现基础的参与贡献,体现高频短周期特性,对高频段激励敏感而容易引发共振。当一种环境激励来临时,往往会诱发另外一种激励(例如:地震来临时会诱发波浪作用,甚至海啸)。与地震作用(例如:卓越频率一般为0.6-10Hz范围,具体坐落的场地的软硬程度直接有关[7])特性相比,波浪作用(例如:卓越频率一般为0-1.5Hz左右,与具体浪高有关)的卓越频段较低,地震作用对风机结构高、低频振型动力特性均有贡献,波浪力对塔筒参与较多的低频动力贡献较多且带着下部基础运动。可以说,这样客观而同时发生的两种作用对结构体系的作用分工明确,且相互影响。因此,只关注海上风力发电结构体系承受单一的地震作用,存在着一定的不足或局限性。 基于以上分析,本文针对海上复合筒型基础风力发电结构体系,开展地震和波浪力共同作用下体系动力反应研究,内容包括如下几方面:首先,为了模型建立的合理与便利性,开发了塔筒-筒型基础-地基-透射边界的可视化智能建模程序TJU.WPS(Wind Power Structure)。然后,为了充分考虑波浪力作用,生成不同震级地震作用下的不同高度位置的波浪力时程。结合地震和波浪力两种激励分析结构体系动力特性并给出理论解释。最后,计算地震和波浪共同作用下这种结构体系的动力反应,进一步分别在性质和量化角度研究了结构动力反应对波浪力的敏感性。同时对极端地震作用下风电结构的倒塌模式进行了分析。 结论 本文对近海风电结构体系的智能建模、动力特性与地震波浪作用下的倒塌模式进行了研究,简要总结如下: (2)指出了天津波、迁安波、Taft波三种典型地震动作用下风机结构振动的频域特点。同时,结合理论,解释了大震过程中风机塔筒响应的一些典型现象。 (3)强调了波浪力的不容忽视性:与单独输入地震波相比,波浪力能够显著改变结构动力响应功率谱中能量的分布。 (4)论述了三种典型地震动作用下风机结构体系的破坏模式相同点及其区别:超大震作用下风机结构都将脱开地基向上运动,最终回落到地基,不同典型地震动下风机结构脱开地基对应的时刻以及脱开地基的幅度不同。另外,计算结果给出了引起风机结构倒塌破坏不同典型地震动的最小峰值。 参考文献(References): [1] 陈为飞. 近海风机塔架风浪荷载分析[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2010. Chen Weifei. Analysis of wind and wave loads on offshore wind turbine towers [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2010. [2] 李德源, 刘胜祥, 张湘伟. 海上风力机塔架在风波联合作用下的动力响应数值分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2009, 45(12): 46-52. Li Deyuan, Liu Shengxiang, Zhang Xiangwei. Dynamical response numerical analysis of the offshore wind turbine tower under combined action of wind and wave[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 45(12): 46-52. [3] 于通顺,王海军.循环荷载下复合筒型基础地基孔隙水压力变化及液化分析[J].岩土力学,2014,35(3):820-826. YU Tong-shun, WANG Hai-jun. Pore water pressure fluctuation and liquefaction analysis of subgrade for composite bucket foundation under cyclic loading [J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(3):820-826. [4] Cheng, PW. A reliability based design methodology for extreme responses of offshore wind turbine[D]. PhD Dissertation, Delft University, 2002. [5] Bazeos N, Hatzigeorgiou G D, Hondros I D, et al. Static, seismic and stability analyses of a prototype wind turbine steel tower[J]. Engineering Structures, 2002, 24(8): 1015-1025. [6] 赖伟, 王君杰, 胡世德. 地震下桥墩动水压力分析[J]. 同济大学学报, 2004, 32(1): 1-5. Lai Wei, Wang Junjie, Hu Shide. Earthquake induced hydrodynamic pressure on bridge pier[J]. Journal of Tongji University, 2004, 32(1): 1-5. [7] 卢明奇, 杨庆山. 地震作用下相邻建筑结构的最大相对位移[J]. 土木工程学报, 2012, 45(3): 74-78. Lu Mingqi, Yang Qingshan. Maximum relative displacement between adjacent structures during ground motions[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2012, 45(3): 74-78. [8] Lian Jijian, Ding Hongyan, Zhang Puyang,et al. Design of large scale prestressing bucket foundation for offshore wind turbine. Transactions of Tianjin University, 2012, 18(2):79-84. [9] Lian Jijian, Ding Hongyan. Research report on the composite bucket foundation for offshore wind turbines[R].Tianjin University, 2010. [10] 杜修力, 赵源, 李立云. 土体-结构界面接触对地下结构动力反应的影响[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报, 2010, 30(5): 471-478. Du Xiuli, Zhao Yuan, Li Liyun. Contact effect of interfaces between soil and structure on dynamic responses of underground structures[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2010, 30(5): 471-478. [11] 刘晶波, 王振宇, 杜修力, 杜义欣. 波动问题中的三维时域粘弹性人工边界[J]. 工程力学, 2005, 22(6): 46-51. Liu Jingbo, Wang Zhenyu, Du Xiuli, Du Yixin. Three-dimensional visco-elastic artificial boundaries in time domain for wave motion problems[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2005, 22(6): 46-51. [12] 谷音, 刘晶波, 杜义欣. 三维一致粘弹性人工边界及等效粘弹性边界单元[J]. 工程力学,2007 ,24 (12) 31-37. GU Yin, LIU Jingbo, DU Yixin. 3D consistent viscous-spring artificial boundary and viscous-spring boundary element[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2007,24 (12) 31-37. [13] 柳国环, 李宏男, 林海. 结构地震响应计算模型的比较与分析[J]. 工程力学, 2009 (2): 10-15. Liu Guohuan, Li Hongnan, Lin Hai. Comparison and evaluation of models for structural seismic responses analysis[J]. Engineering Mechanics , 2009 (2): 10-15. |
||||||
| welcome to www.liuguohuan.net |
| 天津大学 建筑工程学院 ; 天津大学 前沿技术研究院; 国家重点实验室-水利工程仿真与安全 |